What Happens if You Miss a Credit Card Payment?
Citi is an advertising partner.
There are three ways a late or missed payment can impact you financially:
- You may have to pay a late payment fee.
- The interest rate on your credit card may go up to the penalty rate.
- Your credit card issuer might report the late payment to the credit bureaus, which can damage your credit score.
Let’s take a look at the financial consequences of late credit card payments, when they occur and what you need to know.
| How late is your payment? | Potential consequences | Financial impact |
|---|---|---|
| 1 - 30 days | Late payment fee | $25 - $40 |
| 30 - 60 days |
|
|
| 60+ days |
|
|
Late payment fees
Credit card companies often charge a late fee for a missed credit card payment. Late fees typically range from $25 to $40.
Of the three potential consequences of late payments, the penalty fee will likely have the smallest impact on your finances. It’s a simple, one-time charge.
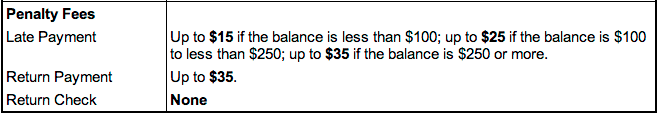
What can you do about late payment fees?
If this is the first time you’ve missed a payment, consider contacting the credit card company to ask if they will waive the late fee. While there’s no guarantee, card companies can sometimes be flexible about fees, especially if you have a long history of paying your card on time. They might be willing to work with you to remove the charge.
If you’re planning to keep your card for a while, the Discover it® Secured Credit Card could cost less in the long run than the AvantCard Credit Card.
![]() Learn more about how to use a credit card.
Learn more about how to use a credit card.
Penalty APR
If you are more than 60 days late on a credit card payment, many cards will switch your credit card APR from the rate you initially agreed upon to the penalty or default APR. This APR will be significantly higher than the regular interest rate you were paying on your card. The penalty APR is typically around 30% or more.

Recovering your original purchase APR
Making continued payments on time is the only way to get the penalty rate removed. You’ll need to pay six consecutive billing periods on time to have your interest rate reverted back to the original offer.
![]() Interested in credit cards with low purchase APRs? See our picks for the best low interest credit cards.
Interested in credit cards with low purchase APRs? See our picks for the best low interest credit cards.
Impact to your credit report and credit score
While the late fee is a one-time payment and the penalty APR will generally only apply to that card alone, late payments of more than 30 days are reported to the credit bureaus and will be reflected on your credit report. 35% of your credit score is based upon your payment history, so late payments on your credit report will reduce your credit score. The more late payments you have and the later they are, the more damage you’ll do to your score.
![]() Read our study about how a missed payment can affect your credit score.
Read our study about how a missed payment can affect your credit score.
A lower credit score will impact the likelihood that you will be approved for a credit card, mortgage or loan in the future. It can also determine the interest rate that you pay if you get approved for a card, loan or mortgage. Generally, you’ll have to pay higher interest rates if you have a lower credit score.
![]() Learn more about how to improve your credit score.
Learn more about how to improve your credit score.
What to do if you miss a credit card payment
- Make the minimum payment as soon as possible. The sooner you make your payment, the fewer repercussions you’ll face. If you missed your credit card payment by one day, don’t sweat it. At most, you’ll be responsible for paying a late payment fee.
- Review your credit card agreement for late payment fees and penalty interest rates. Some cards don’t charge late fees or penalty APRs. The best way to know if you’ll be responsible for additional fees and higher interest rates is to review your card agreement.
- Call your credit card company to ask them to waive your late fee (if there is one). A 2021 LendingTree study showed that this request was granted 88% of the time.
- Make a plan to submit future payments on time. Future on-time payments will help you avoid late fees, recover your original interest rate and rebuild your credit score. Consider putting your credit card bill on autopay so that you don’t miss any more payments. If you’re having a hard time making the minimum payment, build a budget to pay off your credit card debt.
Frequently asked questions
Credit card payments are considered late if they’re not received by the due date listed on your credit card statement.
A credit card’s grace period is a period when interest is waived, typically between the end of your credit card’s billing cycle and when your payment is due. At the end of the billing cycle, you’ll receive a statement with how much you owe. You’ll then have the duration of the grace period — a minimum of 21 days — to pay your credit card before your payment is considered late. If you make your payment past the grace period, you will owe interest for the entire period, plus penalty fees if your card has them.
The content above is not provided by any issuer. Any opinions expressed are those of LendingTree alone and have not been reviewed, approved, or otherwise endorsed by any issuer. The offers and/or promotions mentioned above may have changed, expired, or are no longer available. Check the issuer's website for more details.
